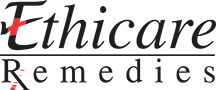Introduction
- An important-and for some prospective patients the most important-question regarding hair restoration surgery is:
- Will it be painful?? Is there any side-effects ?? Is there any guarantee of good result?
- An elective surgical procedure such as hair restoration is one that a potential patient chooses to undergo, in contradistinction with a procedure that the patient needs to undergo
- FUE- Painless,scarless,sutureless ?
- Hair restoration surgery isn’t painless, but pain control is much more effective today than even in the recent past
- Medical research has improved understanding of nociception-how a sensation of pain is received, transmitted and interpreted by nerves from the site of injury to the spinal cord and the brain.
- There is better understanding of the relationship between effective anesthesia and limitation of bleeding or “oozing” during surgery.
- An inadequately anesthetized, anxious patient may have increases in heart rate and blood pressure that increase risk for bleeding; thus, anesthesia level and physical signs such as heart rate and blood pressure are carefully monitored during surgery.
Medications prior to surgery
- Preoperative anxiety about discomfort may be alleviated by administration of anti-anxiety medication.
- Antibiotic, anti-inflammatory, pain killer should be given.
Minimising pain: Increasing comfort
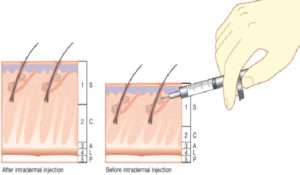
- Topical anesthesia : EMLA cream covered with plastic 45 min-1 hr prior to surgery reduces the painful sensation of needle prick
- Physical stimulation: We use vibrator to minimise the pain of injection
- Melzack and Wall- Gate control theory: Touch, pressure and vibration have the potential to diminish the perception of painful stimuli.
Minimising pain: Increasing comfort
- Needle caliber and rate, depth of injection:
- Smaller caliber needle causes less pain than larger ones, however this potential is only realized if rate of injection is slowed, since a more rapid rate of administration increases the pain.
- We use 30-31 G needle with slow rate of infusion.
- Depth of injection: Initial injections into deeper tissue—-less pain … and then move into superficial planes—–rapid onset and longer duration of anesthesia.
- Office Environment: Anxious patients tend to have more intense pain
- Prior patient education
- Office staff demeanor
- Light music,TV
Comfortable office environment
Local anesthetic:
- LA are divided into two categories- Ester and amide
- In hair transplant we use amide class of anesthetic mostly Lignocaine and bupivacaine
- As they are primarily cleared by hepatic metabolism, patients with liver disease should be treated cautiously.
Lignocaine:
- Most common short acting LA
- Onset of action is 1-4min and duration of action is 120 min when combined with epinephrine
- The recommended max total daily dose (TDD) is 4.5mg/kg(max 300 mg) when used alone and 7mg/kg (max 500 mg) when combined with epinephrine.
Bupivacaine:
- It is the most commonly used long-acting local anesthetic in hair transplantation.
- Onset of action is 5-10min and duration of action is 180-240 min when combined with epinephrine
- The recommended max total daily dose (TDD) is 175 mg without and 200 mg with epinephrine
Max safe daily dose in ml
- Lignocaine = 21.3mg/ml
- So we can use max 500mg= 23.47ml
- Bupivacaine= 5mg/ml
- So we use max 200 mg= 40 ml
Lignocaine:Bupivacaine
- Commonly bupivacaine is combined with lignocaine to achieve quick and prolonged anesthesia
Factors considered in determining max dose:
- General health status, body weight
- Dosing interval, length of surgery
- Anesthetic technique
- Administration of concomitant medications like BZD
Techniques of local anesthesia
- Peripheral nerve block
- Field block
- Tumescent anesthesia
Peripheral nerve block
- It is infiltration of small volume of LA around nerve trunks.
- In hair transplant we give supraorbital,supratrochlear and occipital nerve blocks
NERVE BLOCK advantage
- Can substitute a single injection for a large number of injections and
- anesthetize a large area with a small amount of anesthetic so less volume of local anesthetic required
Rapid onset and prolonged anesthesia
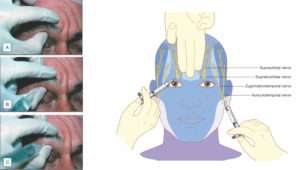
(A) Technique for locating the supraorbital notch. (B) Proper position and direction of needle during infiltration of anesthetic for nerve block. (C) Needle redirected medially to block supratrochlear nerve
Field block
- Field block involve the creation of anesthetised perimeter proximal to an operative field
Different techniques can be used to give field block are-
- Multiple wheal technique
- Continuous wheal technique
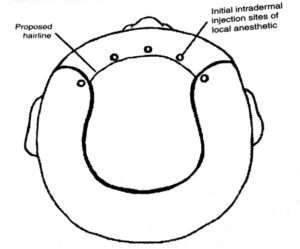
(Fig.Multiple wheal Technique)
Tumescent anesthesia
- It employ large volume of dilute local anesthesia with adrenaline
- It reduce local anesethetic doses, improves pain control and effectively provide hemostasis and clear operative field
- Specially beneficial in body hair transplant where large area to be anesthetised and one can easily cross the same limit of LA
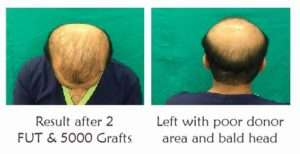
- In previous failure cases, high grade of baldness and cases where body hair transplant is required chances of anesthesia overdose and consequent side effects are higher so thorough knowledge of anesthetic agent- its mechanism of action, dose, route, rate and depth of injection should be well versed.
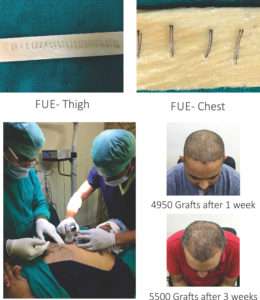
- FUT Disaster @ some other centre
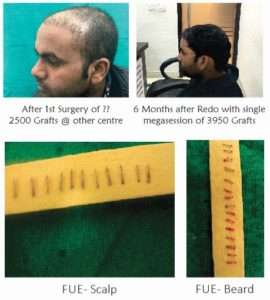
- Correction of previous surgery- single megasession of 3950 Grafts by FUE


Conclusion
- Anxiety about discomfort can be a roadblock. Effective patient/physician communication and rational use of medications can remove the roadblock and open the way to successful hair restoration.